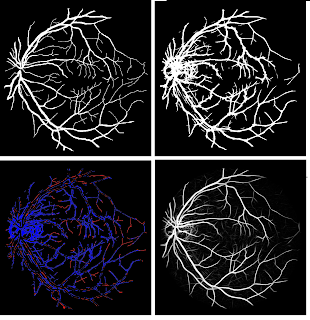
An algorithm is proposed to perform segmentation of blood vessels in 3D breast MRIs. The blood vessels play an essential role as an additional tool to detect tumors. Radiologists use a maximum-intensity projection for the exposure of vasculature. The breast is a challenging organ in detecting vascular structures, because of noise bias and presence of fat tissues. There are several existing algorithms for the detection of blood vessels in MRI images, but these usually prove insufficient when it comes to the breast.
Our algorithm provides a three-dimensional model of the blood vessels by utilizing texture enhancement followed by Hessian-based methods. In addition to this, we tackled blood vessel completion by employing center line tracking, where the seeds are the end points of detached blood vessels found through skeletonizing. The results were compared to the manually segmented golden models defined by radiologists in 24 different patients, which yielded an 86% Sensitivity to the ground truth and 88.3% specificity. It appears that with the application of mass detection as the last step, our algorithm provides a helpful tool for tumour enhancement and automated detection of breast cancer.