Stroke is one of the principal causes of death and disability worldwide. Cerebral ischemia is the result of insufficient cerebral blood flow for cerebral metabolic functions. Oxidative stress and inflammation have an important role in cerebral infarction which mediated by ischemia and reperfusion. Reperfusion injury stimulates many pathological mechanisms such as leukocyte infiltration, oxidative stress, inflammation, destruction of blood-brain barrier, platelet activation, nitric oxide release, and apoptosis. Consequently, potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mediators may be beneficial in the treatment of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. The lack of effective and widely applicable pharmacological treatments for ischemic stroke patients may explain a growing interest in the traditional medicines.
Showing posts with label biomedical engineering online impact factor. Show all posts
Showing posts with label biomedical engineering online impact factor. Show all posts
Monday, 24 July 2017
Wednesday, 14 June 2017
A Revolutionary Method of Treatment
A tumor without a supporting network of blood vessel formation is like a car without wheels-it’s not going anywhere! But the multiple hemangiopericytoma type of brain tumors I’ve been shackled with over the last fourteen years were multiplying rapidly in the cancer lane and were driving me one hundred and ten miles an hour to my grave!
That was until suddenly, in early March, 2003, when Providence unexpectedly whisked me away from my home in Burbank, CA and guided me directly to the one person, who was to change my life forever so that I would be free of any new or recurring tumors of any variety, have a quality life and even have it extended several years! He is Mr. Nick Kostovic, a pioneer and visionary in energetic medicine, and his health clinic, the Bio Technological Health Center, Inc., in San Pedro, California is where he not only killed my malignant brain tumors, but where this brilliant, caring therapist is helping heal my malignant brain tumors, but where this brilliant, caring therapist is helping heal many other patients by eradicating other treacherous life threatening diseases such as diabetes, cancer, Lou Gehrig's Disease (ALS), Parkinson’s, MS, strokes and more.
That was until suddenly, in early March, 2003, when Providence unexpectedly whisked me away from my home in Burbank, CA and guided me directly to the one person, who was to change my life forever so that I would be free of any new or recurring tumors of any variety, have a quality life and even have it extended several years! He is Mr. Nick Kostovic, a pioneer and visionary in energetic medicine, and his health clinic, the Bio Technological Health Center, Inc., in San Pedro, California is where he not only killed my malignant brain tumors, but where this brilliant, caring therapist is helping heal my malignant brain tumors, but where this brilliant, caring therapist is helping heal many other patients by eradicating other treacherous life threatening diseases such as diabetes, cancer, Lou Gehrig's Disease (ALS), Parkinson’s, MS, strokes and more.
Friday, 9 June 2017
Visually Guided Horizontal Saccades under the Double-Step Paradigm
Visually goal-oriented saccades were recorded under the double-step paradigm. Data were analyzed to produce parameter estimates using the system identification technique for a 3rd-order linear horizontal saccadic eye movement model. Statistical analysis of a large human saccade data set provided reliable conclusions of the response properties. Saccade amplitude, latency and inter-saccade interval were discussed with time delay, indicating the parallel programming mechanism, which two saccades to different targets could be programmed simultaneously. The results of neural input estimations suggested that the double-step visual targets may affect the synchronous firing of the saccade responsible neurons in the superior colliculus.
Tuesday, 6 June 2017
Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Smooth Pursuit Eye Movements
Conventional feedback control models of the oculo motor system fail to account for the destabilizing effects of neural transmission delays. To address this shortcoming, a linear quadratic tracking algorithm used to control smoothly pursuing eye movements of various target trajectories is presented.
Based on the type of input to the system, it is shown that stability, in the presence of large motor feedback delays, can be maintained by modulating weighting factors intrinsic to the model. Conditions, such as the initial orientation of the eye relative to the location of where a target first becomes salient and the possible oscillatory nature that the reference trajectory may present, play important roles in determining the optimal cost to go motor control strategy at the onset of a tracking movement.
Friday, 2 June 2017
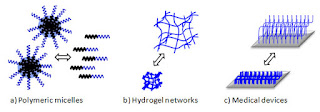
Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels Bearing αamino acid Residues: a Potential Platform for Future Therapies
Vinyl hydrogels bearing α-amino acid residues have been explored as platforms for the treatment of cancer, glaucoma and mood disorder therapies. Ionic/ionizable groups of the L-valine, L-phenylalanine and L-histidine residues are able to modify the swelling properties of the hydrogel on the basis of their thermodynamic characteristics.
Greater basicity constants of functional groups improve a greater loading of the drug and a longer sustained-release pattern. The pH and the temperature affect the swelling of the hydrogel and increase ‘on demand’ the drug availability. A further stimulus based on alternating magnetic fields can be applied on hydrogels containing embedded magnetic nanoparticles used for site-specific controlled drug delivery. The diffusion process for the in vitro release of the drug (cisplatin, doxorubicin, pilocarpine, trazodone, citalopram and paroxetine) from the drug loaded hydrogels is mainly controlled by the drug-polymer interaction, that in the meanwhile preserves its bioactivity. The different interaction strength between the drug and the polymer may be a strategy to develop suitable capsules for long-term therapies.
Wednesday, 31 May 2017
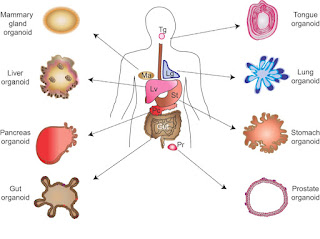
Human-Organoid Models: Accomplishments to Salvage Test-Animals
Late
stage attritions in drug discovery are costly and consuming. Improbable
response of test molecules acquired in non-human systems is attributed to be
the major cause of clinical failures. While conventional in vitro methods of drug discovery do not truly represent the human system, the animal models used
for in vivo validation are also genetically and phenotypically distant from
humans.
However, recent developments in organoid culture are motivating and
elevate hopes for replacing test animals with artificial human tissue models.
Possibility of creating functional tissue ex vivo has a potential to
revolutionize the way human therapeutics is perceived. Not only will it bridge
the gap between drug development and its clinical efficacy but also help
strategizing regenerative medicine. Successful human-tissue surrogates would liberate test animals or at least minimize their use for research purposes.
Potential drug candidates tested on human-tissue equivalents are expected to generate
clinically much more relevant data. Here we deliberate upon the options and
possibilities of accomplishing human organoid models for in vitro testing and
their significance in therapeutics.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)