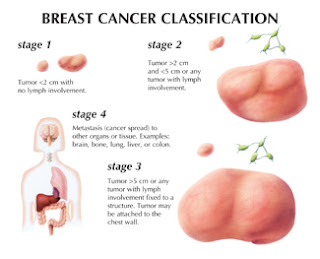
Breast cancer is a leading fatality cancer for woman. According to epidemiological data, breast cancer accounts for 20-25% of female malignant tumor, with is expected to increase. These facts have driven us to select this deadly cancer as our domain. Breast cancer has four early signs; micro-calcification, mass, architectural distortion and breast asymmetries. However, only data regarding mass will be used as a pilot project to test our system later on. Masses of 2 cm in diameter are palpable with regular breast self-examination while mammogram images can capture it from 5 mm in diameter.
However, these images were to be determined by an expert radiologist who is familiar with breast cancer. Generally, there are 2 types of breast cancer which are in situ and invasive. In situ starts in the milk duct and does not spread to other organs even if it grows. Invasive breast cancer on the contrary, is very aggressive and spreads to other nearby organs and destroys them as well. It is very important to detect the cancerous cell before it spreads to other organs, thus the survival rate for patient will increase to more than 97%. However, time taken from taking mammogram images to biopsy dangerous result varies between 2weeks to a month in average.