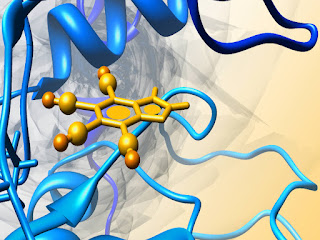
Drug designing and molecular dynamic studies were an intense, lengthy and an interdisciplinary venture. At present, a new approach towards the use of computational chemistry and molecular modeling for in-silico drug design. Computational in-silico drug design skills are used in bioinformatics, computational biology and molecular biology.
Drug designing using in-silico methods is cost effective in research and development of drugs. Currently, a vast number of software’s used in drug design. In-silico drug designing and molecular dynamic studies can be performed by using different methods namely homology modeling, molecular dynamic studies, energy minimization, docking and QSAR etc. By using in-silico drug designing we can produce an active lead molecule from the preclinical discovery stage to late stage clinical development. The lead molecules which are developed will help us in selection of only potent leads to cure particular diseases. Therefore in-silico methods have been of great importance in target identification and in prediction of novel drugs.