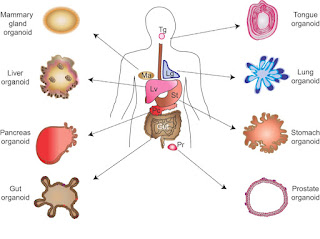
However, recent developments in organoid culture are motivating and
elevate hopes for replacing test animals with artificial human tissue models.
Possibility of creating functional tissue ex vivo has a potential to
revolutionize the way human therapeutics is perceived. Not only will it bridge
the gap between drug development and its clinical efficacy but also help
strategizing regenerative medicine. Successful human-tissue surrogates would liberate test animals or at least minimize their use for research purposes.
Potential drug candidates tested on human-tissue equivalents are expected to generate
clinically much more relevant data. Here we deliberate upon the options and
possibilities of accomplishing human organoid models for in vitro testing and
their significance in therapeutics.
At
the end of a mountain road in Austria during the summer of 2003, I waited for a
boat with my family on a dock at a large lake. Suddenly I saw a man fall to the side walk. His skin had turned that ashen blue color, and it was clear to me
that he was in cardiac arrest. There was a crowd of more than 75 persons just
standing and looking at him.
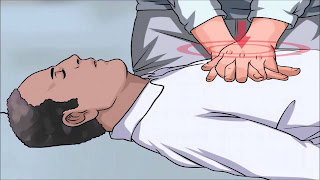
I knew what to do when there was no detectable
pulse or breathing. Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) chest compressions
were started immediately. His skin color returned to nearly normal. After a few
minutes, a single bystander came up and said they knew how to do breaths. At that time, recommendations were for intermittent breathing as well as chest compressions. The stricken person made it alive to the EMS vehicle that took
nearly 30 minutes to arrive. While I do not know the eventual outcome, I do know
he was successfully resuscitated using an Automated External Defibrillator
(AED). Furthermore with the quick application of CPR, he likely had a full
recovery. Unfortunately, from the crowd response at that time, there were not
enough people trained to act in this emergency situation where seconds really
count.
Goal-oriented
human saccades were recorded under double-step paradigm. The stimuli consisted
of either visual or auditory-visual bi-sensory targets. Eye movement data were analyzed based on a 3rd-order linear horizontal saccadic eye movement model,where the inputs to the muscle were agonist and antagonist active-state
tensions that were described by pulse-slide-step wave forms with a post
inhibitory rebound burst (PIRB) based on a time optimal controller. Parameter
estimations were calculated using the system identification technique for
saccade parameters and neural inputs. Saccade amplitude transition function
(ATF) and response latency indicated the saccade programming mechanism. The
responses were affected by when the second peripheral target was presented.
Protein
trafficking or protein sorting is the mechanism by which a cell transports
proteins to the appropriate position in the cell or outside of it. This
targeting is based on the information contained in the protein. Many methods predict the sub cellular location of proteins in eukaryotes from the sequence information. However, most of these methods use a flat structure to perform
prediction. In this work, we introduce ensemble methods to predict locations in
the eukaryotic protein-sorting non membrane pathway hierarchically.
A
novel, non-contact ultrasound device is detailed for recording and analyzing 3D
fast eye movements (saccades) and smooth pursuit eye movements. Saccades are
studied to gain a better understanding of the human oculomotor plant and
neuromuscular systems. Abnormal saccades can be indicators of both neurological disorders and mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI). Limitations in existing
saccade measurement devices prevent them from being used to measure saccades
immediately after a possible MTBI event or easily outside of the clinical
environment.

Data obtained indicated no cytotoxic
response in control cells, as the viability of cells without treatment with AF
standard or methanolic extracts of AF extracts [negative control] using
methanol as the reconstituting solvent, was 99.9% after 24 hrs. of incubation.
However, cell viability significantly (p<0.001) decreased upon exposure to AF extracts especially for poultry feed. This was influenced by both the dose
and duration of exposure, which was much more pronounced when the cells were
exposed to AFB1 standard than for all the AF extracts tested. This implies that
these feeds on exposure to AF can greatly influence animal health with respect
to both the contamination dose and exposure time.

We propose that bioengineered cranial bones with multiple
intelligent functions, including site specific Tran’s meningeal drug delivery
and neurotoxin drainage with EEG feedback, can provide effective treatment of these
brain disorders by drug combinations that act on both synapses and genes with
concomitant selective drainage of harmful extracellular molecules. After examining and summarizing the rationale and feasibility of this proposal, we
suggest novel methods for extending the functions of the involved components
including synergies with existing devices and we highlight relevant pre clinical
results, discussing medical prospects of this novel neuro therapeutic approach.
Finally, we discuss key engineering, scientific, clinical and ethical
challenges to introducing bio engineered cranial bones with multiple intelligent
functions to the clinic within a decade.

Histological criteria for the
diagnosis of IDC-P include solid; dense cribriform (>50% cellularity of the
lumen); trabecular/micropapillary; and loose cribriform intraductal proliferation
of malignant cells. The latter two growth patterns share much similarity with HGPIN. In these instances, additional diagnostic criteria, such as marked
nuclear pleomorphism (nuclear enlargement > 6x normal nuclei), and nonfocal
comedonecrosis (> 1 duct showing comedonecrosis) are criteria needed to
differentiate it from HGPIN.
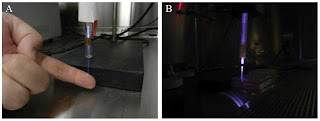
The advantage of cold plasma therapy
over conventional thermal plasma treatments, arc coagulators and desiccators,
is that it allows for more precise application and therefore more controllable
effects on the tissue. Additionally, cold plasma treatment showed stimulatory effects on wound healing and tissue regeneration. Experiments show that cold
atmospheric plasma treatment allows for efficient, non-contact, painless, and
antiseptic effects without damaging healthy tissue. As a result of the better
understanding of complex plasma phenomena and the development of new plasma
sources in the past few years, plasma medicine has developed into an innovative
and promising field of research.
Current methods for the assessment
of the outcome after anterior knee pain or lateral patellar instability
treatment have several limitations, for example their subjectivity. Therefore,
new technologies are needed to objectively evaluate the outcomes of treatments
for patellofemoral disorders.
Kinematic and kinetic analyses during dynamic
activities under realistic loading conditions that trigger or aggravate the
symptoms can: evaluate the patellofemoral patient in an objective way before
surgery; analyse the defense mechanisms the patient develops in order to reduce pain and/or instability; improve our knowledge of the aetiopathogeny and
therefore of a suitable treatment for patellofemoral disorders; and objectively
evaluate the result of the treatment. However, the kinetic and kinematic
analyses are not diagnostic tools.
Data collection for cancer patients
is recognized as an important task in the USA, where the National Program of
Cancer Registries (NPCR) administered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention collects data on the occurrence, type, extent, and location of the
cancer, and the type of initial treatment. The International Consortium for
Health Outcomes Measurements (ICHOM) aims at providing a global resource of
in-use outcome measures and risk adjustment factors by medical condition and
creating a global standard for measuring results.
The double-step auditory stimuli
designed for human triggered saccadic eye movements, detecting each saccade and estimated the saccade response characteristics, namely duration and latency.
Based on the latency, it is possible to determine the type of saccade generated
by the subject through a clustering technique. While keeping their duration
unchanged, the number of double-step saccades rises. The hindsight from this
finding is useful to guide the future stimulus designs to trigger specific
saccade types in humans. It demystifies the nature of dominant saccadic
response as we explore the changes of sounds in any controlled environment.
Modeling the critical issues of the
dynamics of UV-light-initiated crosslinking of corneal collagen including the
new safety criteria, crosslinking time and the efficacy. A coupled dynamic equations is numerically solved and analytic formulas are derived for three critical parameters: the safety dose (E*), the cross linking time (T*)
and the efficacy defined by the increase of corneal stiffness (S). The critical
issues of corneal crosslinking is explored by nine parameters: the three
extinction coefficients, concentration and diffusion depth of the riboflavin
solution, the UV light dose, irradiation duration, the cytotoxic energy threshold
of endothelial cells and the corneal thickness.