Drug designing using in-silico methods is cost effective in research and development of drugs. Currently, a vast number of software’s used in drug design. In-silico drug designing and molecular dynamic studies can be performed by using different methods namely homology modeling, molecular dynamic studies, energy minimization, docking and QSAR etc. By using in-silico drug designing we can produce an active lead molecule from the preclinical discovery stage to late stage clinical development. The lead molecules which are developed will help us in selection of only potent leads to cure particular diseases. Therefore in-silico methods have been of great importance in target identification and in prediction of novel drugs.
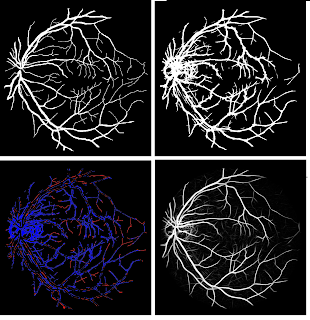
An algorithm is proposed to perform segmentation of blood vessels in 3D breast MRIs. The blood vessels play an essential role as an additional tool to detect tumors. Radiologists use a maximum-intensity projection for the exposure of vasculature. The breast is a challenging organ in detecting vascular structures, because of noise bias and presence of fat tissues. There are several existing algorithms for the detection of blood vessels in MRI images, but these usually prove insufficient when it comes to the breast. Our algorithm provides a three-dimensional model of the blood vessels by utilizing texture enhancement followed by Hessian-based methods. In addition to this, we tackled blood vessel completion by employing centerline tracking, where the seeds are the endpoints of detached blood vessels found through skeletonizing.
Hadoop is one of the reputed general purpose computing platforms used to process big data. Mapreduce is the Hadoop project’s main processing engine that provides a framework for distributed computing. This is generated from the combination of ‘Map’ and Reduce concepts in the functional programming. This functional programming model hides the entire complexities related to distributive computing nodes, so that the developer can focus on the implementation of the Map and Reduce functions.
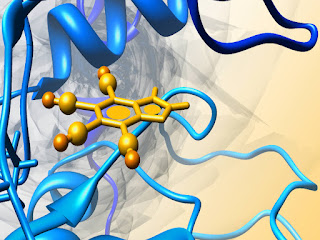
Alzheimer‘s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, encircling the deterioration of cognitive functions and behavioral changes, characterized by the aggregation of amyloid β-protein (Aβ) into fibrillar amyloid plaques in elected areas of the brain with the lipid-carrier protein apolipoprotein E (apoE), the microtubule associated protein tau, and the presynaptic protein α-synuclein. High levels of fibrillary Aβ, the main constituent of senile plaques, are deposited in the AD brain that outcome in the thrashing of synapses, neurons and destruction of neuronal role.

Aβ is derived from the amyloid precursor protein through sequential protein cleavage by aspartyl protease, β-secretase and presenilin-dependent β-secretase triggering a spill of events such as oxidative damage, neurotoxicity, and inflammation that contributes to the progression of AD. Therefore the Aβ protein may be a target for anti-Alzheimer drugs. Aβ protein was retrieved from the Protein data bank and energy minimized and subjected to molecular dynamic simulations using NAMD 2.9 software with CHARMM27 force field in water.