Photo
polymerization has been broadly utilized as a part of uses running from
synthetic designing to biomedical and biomaterials. It has been utilized forcreation of catheters, amplifiers, surgical veils, medicinal channels, andblood investigation sensors. Photopolymers have additionally been investigated
for utilizations in dentistry, drug conveyance, tissue building and cell
exemplification frameworks. Bright, unmistakable and infrared lights (360 to
1000 nm) have been utilized as the photo initiators for different
photosensitizers.
Photo
polymerization has been broadly utilized as a part of uses running from
synthetic designing to biomedical and biomaterials. It has been utilized forcreation of catheters, amplifiers, surgical veils, medicinal channels, andblood investigation sensors. Photopolymers have additionally been investigated
for utilizations in dentistry, drug conveyance, tissue building and cell
exemplification frameworks. Bright, unmistakable and infrared lights (360 to
1000 nm) have been utilized as the photo initiators for different
photosensitizers.Wednesday 31 August 2016
Analytic Formulas for the Clinical Issues of a UV-Light-Activated Corneal Crosslinking Device
 Photo
polymerization has been broadly utilized as a part of uses running from
synthetic designing to biomedical and biomaterials. It has been utilized forcreation of catheters, amplifiers, surgical veils, medicinal channels, andblood investigation sensors. Photopolymers have additionally been investigated
for utilizations in dentistry, drug conveyance, tissue building and cell
exemplification frameworks. Bright, unmistakable and infrared lights (360 to
1000 nm) have been utilized as the photo initiators for different
photosensitizers.
Photo
polymerization has been broadly utilized as a part of uses running from
synthetic designing to biomedical and biomaterials. It has been utilized forcreation of catheters, amplifiers, surgical veils, medicinal channels, andblood investigation sensors. Photopolymers have additionally been investigated
for utilizations in dentistry, drug conveyance, tissue building and cell
exemplification frameworks. Bright, unmistakable and infrared lights (360 to
1000 nm) have been utilized as the photo initiators for different
photosensitizers.Tuesday 30 August 2016
Effective Treatment of Currently Intractable Brain Disorders
Many
neurological and psychiatric disorders with predominantly cerebral cortical
pathology, including most severe strokes, traumatic brain injuries, malignant
brain tumors, intractable focal epilepsies and dementias such as Alzheimer’sdisease are currently difficult, if not impossible, to treat. This causes
suffering in almost 100 million people worldwide.
We propose that bioengineered
cranial bones with multiple intelligent functions, including sitespecific
transmeningeal drug delivery and neurotoxin drainage with EEG feedback, can
provide effective treatment of these brain disorders by drug combinations that
act on both synapses and genes with concomitant selective drainage of harmful
extracellular molecules. After examining and summarizing the rationale andfeasibility of this proposal, we suggest novel methods for extending the
functions of the involved components including synergies with existing devices
and we highlight relevant preclinical results, discussing medical prospects of
this novel neurotherapeutic approach. Finally, we discuss key engineering,
scientific, clinical and ethical challenges to introducing bioengineered
cranial bones with multiple intelligent functions to the clinic within a decade.
Monday 29 August 2016
Horizontal Saccadic Eye Movements to Visual and Auditory-Visual Double-Step Stimuli
Tissue tolerable plasma has been used in preclinical and more
recently in clinical settings for the debridement of dead tissue and the
removal of bacterial biofilms. Cold plasma therapy is an emerging field in
medical sciences; it is mainly due to the beneficial effects that lowtemperature plasma has demonstrated anti-inflammatory, ant tumorigenic and
anti-microbial effects. The advantage of cold plasma therapy over conventional
thermal plasma treatments, arc coagulators and desiccators, is that it allows
for more precise application and therefore more controllable effects on the
tissue.
Thursday 25 August 2016
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation as a Graduation Requirement for Biomedical Engineering Students
At the end of a mountain road in Austria during the summer of
2003, I waited for a boat with my family on a dock at a large lake. Suddenly I
saw a man fall to the sidewalk. His skin had turned that ashen blue color, andit was clear to me that he was in cardiac arrest. There was a crowd of more
than 75 persons just standing and looking at him. I knew what to do when there
was no detectable pulse or breathing.
Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) chest
compressions were started immediately. His skin color returned to nearly
normal. After a few minutes, a single bystander came up and said they knew how
to do breaths. At that time, recommendations were for intermittent breathing as
well as chest compressions. The stricken person made it alive to the EMSvehicle that took nearly 30 minutes to arrive. While I do not know the eventual
outcome, I do know he was successfully resuscitated using an Automated External
Defibrillator (AED). Furthermore with the quick application of CPR, he likely
had a full recovery. Unfortunately, from the crowd response at that time, there
were not enough people trained to act in this emergency situation where seconds
really count.
Wednesday 24 August 2016
The Neural Networks with an Incremental Learning Algorithm
As
breast cancer can be very aggressive, only early detection can prevent
mortality. The proposed system is to eliminate the unnecessary waiting time aswell as reducing human and technical errors in diagnosing breast cancer. The
correct diagnosis of breast cancer is one of the major problems in the medical
field. From the literature it has been found that different pattern recognition
techniques can help them to improve in this domain.
This paper uses the neural
networks with an incremental learning algorithm as a tool to classify a mass in
the breast (benign and malignant) using selection of the most relevant risk
factors and decision making of the breast cancer diagnosis To test the proposed
algorithm we used the Wisconsin Breast Cancer Database (WBCD). ANN with anincremental learning algorithm performance is tested using classificationaccuracy, sensitivity and specificity analysis, and confusion matrix. The
obtained classification accuracy of 99.95%, a very promising result compared
with previous algorithms already applied and recent classification techniques
applied to the same database.
Tuesday 23 August 2016
Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels Bearing αamino acid Residues
Vinyl hydrogels bearing α-aminoacid residues have been
explored as platforms for the treatment of cancer, glaucoma and mood disorder
therapies. Ionic/ionizable groups of the L-valine, L-phenylalanine and
L-histidine residues are able to modify the swelling properties of the hydrogel
on the basis of their thermodynamic characteristics.
Greater basicity constants
of functional groups improve a greater loading of the drug and a longer
sustained-release pattern. The pH and the temperature affect the swelling ofthe hydrogel and increase ‘on demand’ the drug availability. A further stimulus
based on alternating magnetic fields can be applied on hydrogels containing
embedded magnetic nanoparticles used for site-specific controlled drug
delivery.
The diffusion process for the in vitro release of the drug
(cisplatin, doxorubicin, pilocarpine, trazodone, citalopram and paroxetine)
from the drugloaded hydrogels is mainly controlled by the drug-polymerinteraction, that in the meanwhile preservs it’s bioactivity. The different
interaction strength between the drug and the polymer may be a strategy to
develop suitable capsules for long-term therapies.
Monday 22 August 2016
Meta-Analysis of Genomic Data: Between Strengths, Weaknesses and New Perspective
The rapid advances in
high-throughput technologies, such as microarrays have revolutionizing theknowledge and understanding of biological systems and genetic signatures of
human diseases. This has led to the generation and accumulation of a large
amount of genomic data that need to be adequately integrated to obtain more
reliable and valid results than those from individual experiments.
Meta-analysis of microarray data is one of the most common statistical
techniques used for combining multiple data sets. Despite its remarkable
successes in discovering molecular subtypes, underlying pathways and biomarkers
for the pathological process of interest, this method possesses several limitations.
Here, we provided a briefly
overview of current meta-analytic approaches together with the basic critical
issues in performing meta-analysis of genomic data, with the aim of helpingresearchers to evaluate the quality of existing, published data and obtain more
detailed information on what will be the best strategy to adopt to execute a
good meta-analysis.
Friday 19 August 2016
Horizontal Saccadic Eye Movements to Visual and Auditory
Goal-oriented human saccades were
recorded under double-step paradigm. The stimuli consisted of either visual or
auditory-visual bi-sensory targets. Eye movement data were analyzed based on a
3rd-order linear horizontal saccadic eye movement model, where the inputs to
the muscle were agonist and antagonist active-state tensions that were
described by pulse-slide-step waveforms with a post inhibitory rebound burst
(PIRB) based on a timeoptimal controller.
Parameter estimations were calculated
using the system identification technique for saccade parameters and neural
inputs. Saccade amplitude transition function (ATF) and response latency
indicated the saccade programming mechanism.
The responses were affected by
when the second peripheral target was presented. The neural input estimations
supported the responsive neuron populations in the superior colliculus under
different stimulus conditions, and indicated the double-step visual or
auditory-visual stimulus may affect the synchrony of neuron firing. The study
described here expanded our previous work and further supported the muscle
model as well as the theory of the time-optimal saccade controller under physiological
constraints.Read More...
A Bayesian Analysis of Copy Number Variations in Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization Data
Array Comparative Genomic
Hybridization (CGH) has been widely used for detecting genomic copy number
variations (CNVs). The central goal of array CGH data analysis is to accurately
detect homogeneous regions of log intensity ratios which represent relative
changes in DNA copy number. Various methods have been proposed in recent years.
Most methods, however, do not consider correlations of neighboring probe
measurements, and are usually designed for analysis at single sample level
rather than detecting common or recurrent CNVs among multiple samples. We
propose a Bayesian segment-based approach for efficient analysis of array CGH
data. The proposed method is based on simple assumptions but is general enough
to accommodate various spatial correlations among probe measurements.

It also
allows for multiple samples with recurrent CNVs, therefore is able to borrow
strength across samples. In contrast to another probe-based approach developed
in the same Bayesian framework, the segment-based approach parameterizes the
mean log intensity ratios in a more appropriate way, which leads to a posterior
sampling scheme based on reversible-jump Markov chain Monte Carlo. Want To Read More....
Thursday 18 August 2016
An Ultrasound Based Eye Tracking System
A
novel, non-contact ultrasound device is detailed for recording and analyzing 3D
fast eye movements (saccades) and smooth pursuit eye movements. Saccades are
studied to gain a better understanding of the human oculomotor plant and
neuromuscular systems. Abnormal saccades can be indicators of both neurological
disorders and mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
Limitations in existing
saccade measurement devices prevent them from being used to measure saccades
immediately after a possible MTBI event or easily outside of the clinical
environment. The device proposed is portable allowing saccade measurements in
the field to immediately assess neurological dysfunction associated with MTBI.
Ease of use and portability allow collection of data at times and places not
possible with devices currently available. This increased database of saccades
will expand our knowledge of the relationship between saccades and the
neurological functioning of the brain. The focus of this paper is the
development of a finite element model to establish a starting point for such a
design.Read More.....
Wednesday 17 August 2016
Identifying DNA Methylation Variation Patterns to Obtain Potential Breast Cancer Biomarker Genes
Patterns
of DNA methylation in human cells are crucial in regulating tumor growth and
can be indicative of breast cancer susceptibility. In our research, we have
pinpointed genes with significant methylation variation in the breast cancer
epigenome to be used as potential novel biomarkers for breast cancer
susceptibility.
Using the statistical software package R, we compare DNA
methylation sequencing data from seven normal individuals with eight breast
cancer cell lines. This is done by selecting CG sites, or cytosine-guanine pairings,
at which normal cell and cancer cell variation patterns fall in different
ranges, and by performing upper one-tailed chi-square tests.
These selected CG
sites are mapped to their corresponding genes. Using the ConsensusPath Database
software, we generate genetic pathways with our data to study biological
relations between our selected genes and tumorigenic cellular mechanisms. Using
breast cancer-related genes from the PubMeth and GeneCards databases, we have
discovered 26 potential biomarker genes, which are biologically linked to genes
known to be associated with breast cancer. Read More...
Visually Guided Horizontal Saccades under the Double-Step Paradigm
Visually
goal-oriented saccades were recorded under the double-step paradigm. Data were
analyzed to produce parameter estimates using the system identification
technique for a 3rd-order linear horizontal saccadic eye movement model.
Statistical analysis of a large human saccade data set provided reliable
conclusions of the response properties.
Saccade amplitude, latency and
inter-saccade interval were discussed with time delay, indicating the parallel
programming mechanism, which two saccades to different targets could be programmed
simultaneously. The results of neural input estimations suggested that the
double-step visual targets may affect the synchronous firing of the saccade
responsible neurons in the superior colliculus.
Saccades
are the fastest eye movements that enable us to rapidly redirect our line of
sight from one target to another one. They are conjugate and ballistic, with a
typical duration of 30-100 ms and a latency of 100-300 ms when triggered by
visual stimuli. The latency is thought to be the time interval during which the
CNS determines whether to make a saccade, and, if so, calculates the distance
the eyeball is to be moved, transforming retinal errors into transient muscle
activity. Read More.....
Thursday 11 August 2016
Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Smooth Pursuit Eye Movements
Conventional feedback control models
of the oculomotor system fail to account for the destabilizing effects of
neural transmission delays. To address this shortcoming, a linear quadratic
tracking algorithm used to control smoothly pursuing eye movements of various
target trajectories is presented. Based on the type of input to the system, it
is shown that stability, in the presence of large motor feedback delays, can be
maintained by modulating weighting factors intrinsic to the model.
Conditions,
such as the initial orientation of the eye relative to the location of where a
target first becomes salient and the possible oscillatory nature that the
reference trajectory may present, play important roles in determining the
optimal cost to go motor control strategy at the onset of a tracking movement.
Human perception is the process of acquiring, interpreting,
selecting and organizing sensory information to effectively interact with the
environment. It is argued that the ability to perceive and direct visual
attention to an object that warrants more detailed analysis is the most
important of the senses. The oculomotor system has evolved to serve this
purpose and, consequently, has important communicative value for studying
neuromuscular integration.
Research involving sensorimotor control seeks to answer the
fundamental question: How does our brain select inputs to produce a desired
intention and manifest it in the form of movement. The difficulty associated
with this question becomes more apparent for multi-body, multi-dimensional
systems whose equations of motion are nonlinear and coupled. Since the eye is
confined to three rotational degrees of freedom, and because the actions of its
extraocular muscles are direct, the oculomotor system provides an initial
context for gaining insight into more complex strategies of sensorimotor
control.Read More......
Wednesday 10 August 2016
A Discriminative Feature Space for Detecting and Recognizing Pathologies of the Vertebral Column
Each year it has become more and
more difficult for healthcare providers to determine if a patient has a
pathology related to the vertebral column. There is great potential to become
more efficient and effective in terms of quality of care provided to patients
through the use of automated systems. However, in many cases automated systems
can allow for misclassification and force providers to have to review more
causes than necessary. In this study, we analyzed methods to increase the True
Positives and lower the False Positives while comparing them against stateof-
the-art techniques in the biomedical community. We found that by applying the
studied techniques of a data-driven model, the benefits to healthcare providers
are significant and align with the methodologies and techniques utilized in the
current research community.
Over the years there has been an increase in machine learning
(ML) techniques, such as Random Forrest (RF), Boosting (ADA), Logistic (GLM),
Decision Trees (RPART), Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Artificial Neural
Networks (ANN) applied to many medical fields. A significant reason this hasbecome the case is the capacity for human beings to act as diagnostic toolsover time. Stress, fatigue, inefficiencies, and lack of knowledge all become
barriers to high- quality outcomes.
There have been studies regarding applications of data mining
in different fields, namely: biochemistry, genetics, oncology, neurology and
EEG analysis. However, literature suggests that there are few comparisons of
machine learning algorithms and techniques in medical and biological areas. Of
these ML algorithms, the most common approach to develop nonparametric and
nonlinear classifications is based on ANNs.
In general, the numerous methods of machine learning that
have been applied can be grouped into two sets: knowledge-driven models and
data-driven models. The parameters of the knowledge-driven models are estimated
based on the expert knowledge of detecting and recognizing pathologies of the
vertebral column. On the other hand, the parameters of data- driven models are
estimated based on quantitative measures of associations between evidential
features within the data. The classification models used in pathologies of the
vertebral column have been SVM.
Tuesday 9 August 2016
ePhenotyping for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in the Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network
Electronic health records(EHRs) capture a large volume of
clinical and physiologic data, and present a valuable resource for research.
The “electronic Medical Records and Genomics” (eMERGE) Network was organized by
the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) in 2007 to develop,
disseminate, and apply approaches to combine DNA biorepositories with
electronic medical record(EMR) systems for large-scale, high-throughput genetic
research with the ultimate goal of returning genomic testing results to
patients in a clinical care setting.
To accomplish these goals in the eMERGE Network
an important first step is to develop robust algorithms, so called
“ePhenotyping” tools, to identify cases and controls directly from the EHR for
studies on specific diseases and traits. eMERGE ePhenotypes are developed byone or more primary sites, validated at secondary sites and verified at all
other sites that implement them. The results of this rigorous development
effort are accurate, robust algorithms that may be used at other sites outside
the eMERGE Network.
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a chronic progressively
expanding dilatation of the abdominal aorta below the renal arteries and above
the iliac artery bifurcation. The Society of Vascular Surgery guidelines define
an AAA as a dilatation greater than 3 cm in diameter. Most dilatations expand
to exceed the threshold over time and there is an increased risk of rupture
with catastrophic consequences when the diameter exceeds 5.5 cm.
Monday 8 August 2016
Human-Organoid Models: Accomplishments to Salvage Test-Animals
It takes multi million dollars to develop a new drug as an
estimated 1 out of 10,000 chemicals that enter the discovery cycle (Figure 1)
ever reaches the market. The rising percentage of late-stage clinical failures
(50% in phase 3) is also alarming. The imperative reason for such low success is
our inability to represent human tissue in laboratory. Test models like flat
surface cell-culture, virtual computational methods and small animals cannot
replicate human system; as a consequence the outcome has not been clinically
valuable most of the time. Cells accustomed to spatially dynamicmicroenvironment are conventionally studied in isolation; mostly as homogeneous
cultures must not be expected to display bona-fide behavior. Engagement of
cells with immediate extracellular matrix (ECM) and neighboring cells has been
overlooked while evaluating their response to peripheral stimulus; be it in the
form of drug or toxin or intrinsic physiological entities like enzymes and
hormones. Nevertheless, lack of appropriate ECM milieu has impacted least on in
vitro studies related to intracellular molecular-machinery saving us from
getting fundamentally wrong.
Non-availability of a flexible 3D system is attributed to be
the major obstacle in establishing new standards through organotypic cell
culture [3]. Nevertheless, commercial availability of scaffolds like
Ultra-Web®, Extracell®, ECM-analog®, BD-Matrigel®, Corning-Matrigel®, Alvetex®,
BioVaSc®, Algimatrix® and spheroids of 3D-Biotek® that allow organotypic
culture and especially the ones available in conventional plate formats are
expected to change the scene.
A dynamic and reciprocal exchange of information between
cells and ECM contributes significantly in tissue specific gene expression
regulating its morphology and physiology. The hierarchy of ECMmediated
signaling in tissue differentiation and physiology is elegantly demonstrated by
Bissell et althrough ex vivo modeling of milk secreting mammary glands using
Matrigel a tumor derived ECM. We need an efficient cell-interactive scaffold of
benign origin, having good shelf-life and stability, for studying cell-ECM
dynamics in an experimental micro-environment. Adapting organotype culture
could reveal true behavior of cells in real tissue like layout and also
elaborate on contextual cell-cell and cell-ECM dynamic relation. Cell- ECM
dynamics being at the helm of fundamental understanding of normal vs.
abnormal-cell response could thus provide an altogether new meaning to our
approach towards therapeutics. Improved comprehension of bi-directional
relation of cell with its surrounding milieu has a potential to create a new
line of drug design focused on empowering and restoring the natural
microenvironment to revert the unhealthy or diseased condition.
Friday 5 August 2016
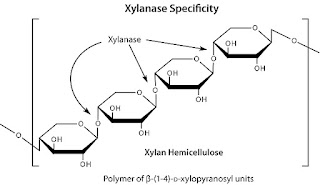
In silico Study of Bacillus brevis Xylanase
The most important building block of
hemicelluloses is xylan. It is broken down into xylose oligomer residues by
Xylanase - an enzyme, produced by most organisms, to utilize xylose as primary
source of carbon. The Xylanase produced are classified into families, viz 5, 8,
10, 11 and 43 - of Glycoside Hydrolases (GH). Xylanase from family GH 11 are
monospecific, they consist solely of Xylanase activity, exclusively active on
D-xylose containing substrates.They are inactive on aryl cellobiosides. The
fungal Xylanase are produced in higher concentrations, as compared to bacterial
Xylanase, but have limited use in pulp bleaching, as they affect the viscosity
and strength of the product. In the present study, we have worked upon the
Xylanase of Bacillus brevis, which is fulfilling all the required quality
needed to be a commercial Xylanase, and thus is used by many industries. The
enzyme, when studied after modelling, provided similar structural configuration
with high stability. When compared with other bacterial and fungal Xylanase
structures, it provided better potential to ‘activity enhancement’ and ‘in
silico handling’.
Hemicellulose is one of the
most important polysaccharide found in the cell wall of the woody plants. It is
made up of various building blocks, which are heteropolysaccharides found along
with cellulose constituting about 20-30% of the wood dry weight. It is the
second most abundant polysaccharide after cellulose. Xylan is built fromhomopolymeric backbone chain of 1, 4-linked β-D-xylopyranose units, including
short chains of O-acetyl, α-L-arabinofuranosyl and D-glucuronyl or
O-methyl-D-glucuronyl residues. Complete degradation of xylan requires a
concerted and synergistic function of several enzymes - including endo-beta-1,
4-D-Xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8). Xylanase break down the xylan into oligoxylose
residues, which are utilized by microbes as primary source of carbon.
Different types of Xylanase
have been grouped under the category of Glycoside Hydrolases (GH), which are
further classified into various families. These families are classified on the
basis of similarities in their amino acid sequences and hydrophobic cluster
analysis. Xylanase are classified into many families like 5, 8, 10, 11 and 43
of Glycoside Hydrolases. Xylanase are also classified into two groups, based on
their molecular weight and pI. One group has low molecular weight <30 kDa
and basic pI, while the other group has higher molecular weight >30 kDa and
acidic pI. Xylanase from family 10 (GH10) and family 11 (GH11) of Glycoside
Hydrolases are the major and beststudied Xylanase.
Get PDF File Here
Wednesday 3 August 2016
A Revolutionary Method of Treatment
A tumor without a supporting network of blood
vessel formation is like a car without wheels-it’s not going anywhere!
That was until suddenly, in early March, 2003,
when Providence unexpectedly whisked me away from my home in Burbank, CA and
guided me directly to the one person, who was to change my life forever so that
I would be free of any new or recurring tumors of any variety, have a quality
life and even have it extended several years! He is Mr. Nick Kostovic, a
pioneer and visionary in energetic medicine, and his health clinic, the Bio
Technological Health Center, Inc., in San Pedro, California is where he not
only killed my malignant brain tumors, but where this brilliant, caring
therapist is helping heal my malignant brain tumors, but where this brilliant,
caring therapist is helping heal many other patients by eradicating othertreacherous lifethreatening diseases such as diabetes, cancer, Lou Gehrigs
Disease (ALS), Parkinson’s, MS, strokes and more.
There I found the most
knowledgeable, unusual, gifted, medical healer I’ve ever met in all my years of
involvement with traditional medicine. This is not to say Western medicine
hasn’t helped me in many life threatening crises, it has. What I am saying is
that those doctors were not able to heal me as completely as this man has.
A deeply spiritual man once said that “The
ultimate, unique sense of an event, and this very truth of the event, will
communicate itself only and always when the subject experiencing the event
gives himself up to it, all the while trying to understand it. An event revealsitself to those who actively experience it; it reveals itself only in a genuineexperience that rises to the level of the event…” These were the experiences I
was to share with Nick Kostovic, a man of great humility and vast knowledge. He
inspired me to “rise to the event” by trusting him and God.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)