The most important building block of
hemicelluloses is xylan. It is broken down into xylose oligomer residues by
Xylanase - an enzyme, produced by most organisms, to utilize xylose as primary
source of carbon. The Xylanase produced are classified into families, viz 5, 8,
10, 11 and 43 - of Glycoside Hydrolases (GH). Xylanase from family GH 11 are
monospecific, they consist solely of Xylanase activity, exclusively active on
D-xylose containing substrates.They are inactive on aryl cellobiosides. The
fungal Xylanase are produced in higher concentrations, as compared to bacterial
Xylanase, but have limited use in pulp bleaching, as they affect the viscosity
and strength of the product. In the present study, we have worked upon the
Xylanase of Bacillus brevis, which is fulfilling all the required quality
needed to be a commercial Xylanase, and thus is used by many industries. The
enzyme, when studied after modelling, provided similar structural configuration
with high stability. When compared with other bacterial and fungal Xylanase
structures, it provided better potential to ‘activity enhancement’ and ‘in
silico handling’.
Hemicellulose is one of the
most important polysaccharide found in the cell wall of the woody plants. It is
made up of various building blocks, which are heteropolysaccharides found along
with cellulose constituting about 20-30% of the wood dry weight. It is the
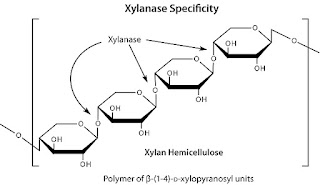
second most abundant polysaccharide after cellulose. Xylan is built fromhomopolymeric backbone chain of 1, 4-linked β-D-xylopyranose units, including
short chains of O-acetyl, α-L-arabinofuranosyl and D-glucuronyl or
O-methyl-D-glucuronyl residues. Complete degradation of xylan requires a
concerted and synergistic function of several enzymes - including endo-beta-1,
4-D-Xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8). Xylanase break down the xylan into oligoxylose
residues, which are utilized by microbes as primary source of carbon.
Different types of Xylanase
have been grouped under the category of Glycoside Hydrolases (GH), which are
further classified into various families. These families are classified on the
basis of similarities in their amino acid sequences and hydrophobic cluster
analysis. Xylanase are classified into many families like 5, 8, 10, 11 and 43
of Glycoside Hydrolases. Xylanase are also classified into two groups, based on
their molecular weight and pI. One group has low molecular weight <30 kDa
and basic pI, while the other group has higher molecular weight >30 kDa and
acidic pI. Xylanase from family 10 (GH10) and family 11 (GH11) of Glycoside
Hydrolases are the major and beststudied Xylanase.
No comments:
Post a Comment