Recent studies have shown the
requirement of a nonlinear revision for linear theory of Bunsen Roscoe law to establish optimal concentration and UV dose for maximum stiffness increasing.
Even the analytic formulas can provide useful guidance in designing protocols
and in optimizing corneal cross linking.
Monday, 31 October 2016
Thursday, 27 October 2016
A Discriminative Feature Space for Detecting and Recognizing Pathologies of the Vertebral Column
Over the years there has been an
increase in machine learning (ML) techniques, such as Random Forrest (RF),
Boosting (ADA), Logistic (GLM), Decision Trees (RPART), Support Vector Machines(SVM), and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) applied to many medical fields. A
significant reason this has become the case is the capacity for human beings to
act as diagnostic tools over time. Stress, fatigue, inefficiencies, and lack of
knowledge all become barriers to high- quality outcomes.
There
have been studies regarding applications of data mining in different fields,
namely: biochemistry, genetics, oncology, neurology and However, literature
suggests that there are few comparisons of machine learning algorithms and
techniques in medical and biological areas. Of these ML algorithms, the most
common approach to develop nonparametric and nonlinear classifications is based
on ANNs.
Tuesday, 25 October 2016
The Neural Networks with an Incremental Learning Algorithm Approach for Mass Classification in Breast Cancer
Breast
cancer is a leading fatality cancer for woman. According to epidemiological
data, breast cancer accounts for 20-25% of female malignant tumor, with is
expected to increase. These facts have driven us to select this deadly cancer as our domain. Breast cancer has four early signs; micro-calcification, mass,
architectural distortion and breast asymmetries. However, only data regarding
mass will be used as a pilot project to test our system later on.
Masses of 2
cm in diameter are palpable with regular breast self-examination while
mammogram images can capture it from 5 mm in diameter. However, these images
were to be determined by an expert radiologist who is familiar with breast cancer.
Generally, there are 2 types of breast cancer which are in situ and invasive.
In situ starts in the milk duct and does not spread to other organs even if it
grows. Invasive breast cancer on the contrary, is very aggressive and spreads
to other nearby organs and destroys them as well.
Monday, 24 October 2016
A Review on New Horizons of Bioinformatics in Next Generation Sequencing, Viral and Cancer Genomics
Genomics
and molecular biology has always been a constant source of inspiration and
motivational research for worldwide researchers in field of biology and
biotechnology. These two fields have always generated a huge amount of data and in order to compile and analyse those, bioinformatics came into action during last decade. Implementation of bioinformatics has a clear intention of doing
all these analysis of data in efficient and fast manner in order to cut down
the expensive laboratory equipment, chemicals and most precious time.
Mostly
genomic data is composed of sequencing results at a higher scale and that is
why manual curating and handling of these data is quite difficult. Supreme aim of this review is to make awareness about bioinformatics options in cancer genomics and viral genomics apart from next generation sequencing. Next
generation sequencing or high throughput sequencing has helped a lot to replace
old conventional method of sequencing and with the help of recent advances in
technologies.
Friday, 21 October 2016
Check this man made wonder device for treating Intractable Brain Disorders
Many
neurological and psychiatric disorders with predominantly cerebral cortical
pathology, including most severe strokes, traumatic brain injuries, malignant brain tumors, intractable focal epilepsies and dementias such as Alzheimer’s disease are currently difficult, if not impossible, to treat. This causes
suffering in almost 100 million people worldwide.
We propose that bioengineered
cranial bones with multiple intelligent functions, including site specific Tran’s meningeal drug delivery and neurotoxin drainage with EEG feedback, can provide
effective treatment of these brain disorders by drug combinations that act on
both synapses and genes with concomitant selective drainage of harmful
extracellular molecules.
Thursday, 20 October 2016
Drug delivery potential of hydrogels having α-amino acid residues
Stimuli-Responsive
Hydrogels such as Vinyl hydrogels bearing α-amino acid residues are Potential vehicles for the drug delivery
systems especially cisplatin, pilocarpine, doxorubicin, citalopram, trazodone,
paroxetine etc. These gels not only transport the drug to the target site but
also preserve the structure and function of drug.
Monday, 17 October 2016
Selenoergothionein as a Potential Inhibitor against Amyloid β-Protein (Aβ): Docking and Molecular Dynamics Studies
Alzheimer‘s
disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, encircling the
deterioration of cognitive functions and behavioral changes, characterized by
the aggregation of amyloid β-protein (Aβ) into fibrillar amyloid plaques in
elected areas of the brain with the lipid-carrier protein apolipoprotein E
(apoE), the microtubule associated protein tau, and the presynaptic protein
α-synuclein.
High levels of fibrillary Aβ, the main constituent of senile
plaques, are deposited in the AD brain that outcome in the thrashing of
synapses, neurons and destruction of neuronal role. Aβ is derived from the amyloid precursor protein through sequential protein cleavage by as partylprotease, β-secretase and presenilin-dependent β-secretase triggering a spill
of events such as oxidative damage, neurotoxicity, and inflammation that
contributes to the progression of AD. Therefore the Aβ protein may be a target
for anti-Alzheimer drugs. Aβ proteinwas retrieved from the Protein data bankand
energy minimized and subjectedto molecular dynamic simulations using NAMD 2.9
software with CHARMM27 force field in water.
Friday, 14 October 2016
A Review on New Horizons of Bioinformatics in Next Generation Sequencing, Viral and Cancer Genomics
Genomics and molecular biology has always been a constant
source of inspiration and motivational research for worldwide researchers in
field of biology and biotechnology. These two fields have always generated a huge amount of data and in order to compile and analyze those, bioinformatics came into action during last decade.
Implementation of bioinformatics has a
clear intention of doing all these analysis of data in efficient and fast
manner in order to cut down the expensive laboratory equipment, chemicals and
most precious time. Mostly genomic data is composed of sequencing results at a higher scale and that is why manual curating and handling of these data is quite difficult. Supreme aim of this review is to make awareness about
bioinformatics options in cancer genomics and viral genomics apart from next
generation sequencing.
Thursday, 13 October 2016
DNA/RNA Fragmentation and Cytolysis in Human Cancer Cells Treated with Diphthamide Nano Particles Derivatives
Molecular structure activity studies for some Diphthamide
Nano particles derivatives indicate that the conformational characteristics
along with the nature and position of the substituents on the Diphthamide Nano
particles derivatives ring play an important role in their biological and
biochemical activities (Figure 1). Therefore, we have calculated the optimized molecular geometries of some Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives.
Calculations are carried out on the structures of these medical, medicinal and
pharmaceutical Nano drugs using Hartree–Fock calculations and also Density
Functional Theory (DFT) by performing HF, PM3, MM2, MM3, AM1, MP2, MP3, MP4,
CCSD, CCSD(T), LDA, BVWN, BLYP and B3LYP levels of theory using the standard
31G, 6–31G*, 6–31+G*, 6–31G(3df, 3pd), 6–311G, 6–311G* and 6–311+G* basis sets
of the Gaussian 09. The comparative heats of formation and Natural Bond Orbital(NBO) charges are calculated for these Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives.
We have finally obtained some conformational rules in terms of the natures and
positions of the substituents on the Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives
ring.
Wednesday, 12 October 2016
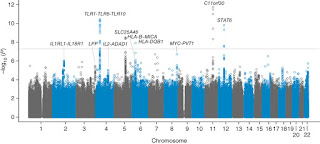
Meta-Analysis of Genomic Data: Between Strengths, Weaknesses and New Perspective
The rapid advances in high-throughput technologies, such as
microarrays have revolutionizing the knowledge and understanding of biological
systems and genetic signatures of human diseases. This has led to the generation and accumulation of a large amount of genomic data that need to beadequately integrated to obtain more reliable and valid results than those from individual experiments. Meta-analysis of microarray data is one of the most
common statistical techniques used for combining multiple data sets.
Despite
its remarkable successes in discovering molecular subtypes, underlying pathways
and biomarkers for the pathological process of interest, this method possesses
several limitations. Here, we provided a briefly overview of current meta-analytic approaches together with the basic critical issues in performing meta-analysis of genomic data, with the aim of helping researchers to evaluate the quality of
existing, published data and obtain more detailed information on what will be
the best strategy to adopt to execute a good meta-analysis.
Friday, 7 October 2016
Human Organoid models may boost the drug discovery & Development
Drug discovery is an expensive affair that involves millions
of dollars. Despite intensified researches, only one out of 10,000 drugs enters
the market after successfully completing series of regulatory measures.
The main reasons for the low rate of success in the drug
discovery include our inability produce the human tissue for research. Test models like flat surface cell-culture, virtual computational methods and small animals are unable to replace the human culture. Recent developments and advancements in the drug research in the form
of Organoid culture is offering new hopes for the drug discovery as there is
scope for using artificial human tissue models in the place of animal models.
There are proposals to create human Organoid models for in vitro testing, which
are expected to add significance to the drug research.
Thursday, 6 October 2016
Application of software tools in the development of novel drug for Breast Cancer
The DNA methylation, in human cells regulates tumor growth
and it also indicates the breast cancer susceptibility. In a research they pinpointed the genes that are involved invariations that occur in methylationof the breast cancer epigenome. The DNA methylation(CG sites)sequences from
7-normal individuals and 8-breast cancer patients were compared by using
Statistical software package R and by Upperone-tailed chi-square tests.
Consensus Path Database is used to map selected CG sites to study the
biological relations between healthy individuals with patients affected by
tumour. Based on the data collected from PubMed and Gene Card, 26 potential
biomarker genes were discovered. All these data helps in the development of
novel treatments for breast cancers.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)