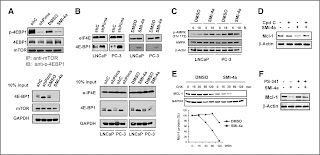
QSAR has established itself as an
important means of virtual screening. Computational analysis of numerous drug molecules aided the facility to meaningfully screen specific ones for further use and experimentation.
In this study, three-dimensional quantitative
structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) associated simulations were done and
stochastic models were developed considering 55 molecules of hydroxyflavanone,
thaizolidene2, 4-dione, pyridone derivatives against proviral insertion site of moloney murine leukemia virus. As part of the study, molecular field analysis
(MFA) was done along with receptor surface analysis (RSA). Moreover, the
generalization ability of the developed model was rigorously validated using 12
test set molecules.