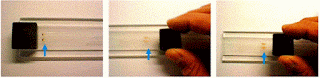
Preliminary development of a simple mesofluidic multi-channel
plastic cartridge with underlying external magnet to drag DNA aptamer-coated
paramagnetic beads through fluids in the channels while developing a sandwich
assay with quantum dot-conjugated reporter aptamers is described.
This approach
is superior to traditional lateral flow test strips in several ways including:
- The ability to control the speed of lateral flow in the channel versus conventional nitrocellulose analytical membranes with fixed wicking times.
- The use of aptamers for potentially greater affinity and consistency from batch-to-batch versus comparable antibodies.
- Superior fluorescence efficiency and intensity provided by quantum dots versus conventional fluorescent dyes and
- The ability to multiplex based on the various colored emissions of different sized quantum dots when excited with a single ultraviolet source.
Development of the system from concept to prototype isdescribed along with illustration of sensitive system performance for severalfood safety-related targets. The system is also clearly adaptable to rapid
multiplex detection and sensitive quantitation of clinical biomarkers, drugs,
environmental, veterinary or other target analytes.