Genomics and molecular biology has
been a source of inspiration for biology and biotechnology research worldwide.
Scientists and the researchers are unable to analyze this huge data manually so that innovative theraputical solutions have emerged for the data analysis.
Bioinformatics come to the rescue of the scientists and researchers in digging
the information efficiently. Bioinformatics is particularly capable of
developing the next generation cancer research from the data and can come with
innovative solutions to cure cancer.
Saturday, 26 November 2016
Friday, 25 November 2016
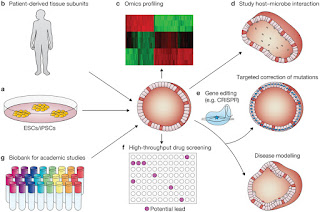
Human-Organoid Models: Accomplishments to Salvage Test-Animals
Late stage attritions in drug
discovery are costly and consuming. Improbable response of test molecules
acquired in non-human systems is attributed to be the major cause of clinical
failures. While conventional in vitro methods of drug discovery do not truly represent the human system, the animal models used for in vivo validation are
also genetically and phenotypically distant from humans. However, recent
developments in organoid culture are motivating and elevate hopes for replacing
test animals with artificial human tissue models.
Possibility of creating
functional tissue ex vivo has a potential to revolutionize the way human
therapeutics is perceived. Not only will it bridge the gap between drug development and its clinical efficacy but also help strategizing regenerative medicine. Successful human-tissue surrogates would liberate test animals or at
least minimize their use for research purposes.
Friday, 18 November 2016
Evaluating the Impact of Different Factors on Voxel-Based Classification Methods of ADNI Structural MRI Brain Images
In this work we introduce the use
of penalized logistic regression (PLR) to the problem of classification of MRI
images and automatic detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Classification of sMRI
is approached as a large scale regularization problem which uses voxels as
input features. We evaluate how differences in sMRI pre-processing steps such
as smoothing, normalization, and template selection affect the performance of
high dimensional classification methods.
In addition, we compared the relative
performance of PLR to a different approach based on support vector machines. To study these questions we used data from the Alzheimer Disease Neuro imaging Initiative (ADNI). The ADNI project follows a protocol consisting of
acquisition of two images in each session, image correction steps and further
evaluation by experts to obtain the optimized images. We evaluated here the
impact of this optimization process on the performance of high-dimensional
machine learning techniques.
Wednesday, 16 November 2016
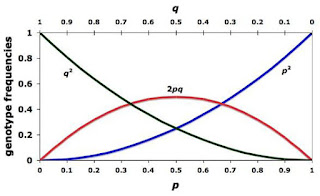
Likelihood Ratio Test of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Using Uncertain Genotypes for Sibship Data
Testing for Hardy-Weinberg
equilibrium of genotype frequencies is a crucial first step in the study of
population genetics. In this paper, we develop an Expectation-Maximization algorithm to estimate the genotype frequencies for sibship data with genotype uncertainty.
We also develop a likelihood ratio test of Hardy-Weinberg
equilibrium for sibships with no parental genotypes available and with possible
genotyping errors. Simulations show that our likelihood ratio test maintains valid control of the type I error rate and good statistical power. Finally, the
likelihood ratio test is extended across strata when a sample is stratified by
multiple ethnic populations with different genotype frequencies.
Wednesday, 9 November 2016
DNA/RNA Fragmentation and Cytolysis in Human Cancer Cells Treated with Diphthamide Nano Particles Derivatives
Molecular structure activity
studies for some Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives indicate that the
conformational characteristics along with the nature and position of the
substituents on the Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives ring play an
important role in their biological and biochemical activities. Therefore, we have calculated the optimized molecular geometries of some Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives.
Calculations are carried out on the structures of these
medical, medicinal and pharmaceutical Nano drugs using Hartree–Fock
calculations and also Density Functional Theory (DFT) by performing HF, PM3,
MM2, MM3, AM1, MP2, MP3, MP4, CCSD, CCSD(T), LDA, BVWN, BLYP and B3LYP levels
of theory using the standard 31G, 6–31G*, 6–31+G*, 6–31G(3df, 3pd), 6–311G,
6–311G* and 6–311+G* basis sets of the Gaussian 09. The comparative heats of formation and Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) charges are calculated for these Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives. We have finally obtained some
conformational rules in terms of the natures and positions of the substituents
on the Diphthamide Nano particles derivatives ring.
Monday, 7 November 2016
Data Inventory for Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy for Outcome Analysis and Modeling
Data collection for cancer patients
is recognized as an important task in the USA, where the National Program of
Cancer Registries (NPCR) administered by the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention collects data on the occurrence, type, extent, and location of the cancer, and the type of initial treatment. The International Consortium for
Health Outcomes Measurements (ICHOM) aims at providing a global resource of
in-use outcome measures and risk adjustment factors by medical condition and
creating a global standard for measuring results.
These initiatives will enable
public health professionals to understand and address the cancer burden more
effectively. We have recently proposed to use the pre-treatment, planning, and
treatment outcomes data for cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy to
provide guidelines for optimal choice of both radiation modality and planning
for new patients. It is important to determine the most influential patient
features (or their combinations) that has the strongest correlation with the
outcomes. We propose an Overlap Volume Histogram as a valuable representation
of size and shape for tumor and organs at risk important for planning.
Friday, 4 November 2016
A new sensitive and rapid assaying technique
Inspite of their low sensitivity
compared to chemiluminescenceand fluorescence methods, Immunochromato graphic(IC) and Lateral flow (LF) test strips are widely used for the rapid detection of drugs, clinical factors, food safety etc. Recently American scientists
developed adaptable rapid quantitation and multiplex detection sensitive assay
for assaying clinical drugs,biomarkers, etc.
Thursday, 3 November 2016
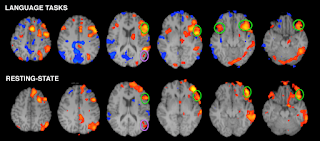
A Similarity Retrieval Tool for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Statistical Maps
We propose a method for retrieving
similar functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) statistical images given a
query fMRI statistical image. Our method thresholds the voxels within those
images and extracts spatially distinct regions from the voxels that remain.
Each region is defined by a feature vector that contains the region centroid,
the region area, the average activation value for all the voxels within that
region, the variance of those activation values, the average distance of each
voxel within that region to the region’s centroid, and the variance of the
voxel’s distance to the region’s centroid.
The similarity between two images is
obtained by the summed minimum distance (SMD) of their constituent feature
vectors. Results and conclusion. Our method is sensitive to similarities in brain activation patterns from members of the same data set. Using a subset of
the features such as the centroid location and the average activation value
(individually or in combination), maximized the sensitivity of our method. We
also identified the similarity structure of the entire data set using those two
features and the SMD.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)